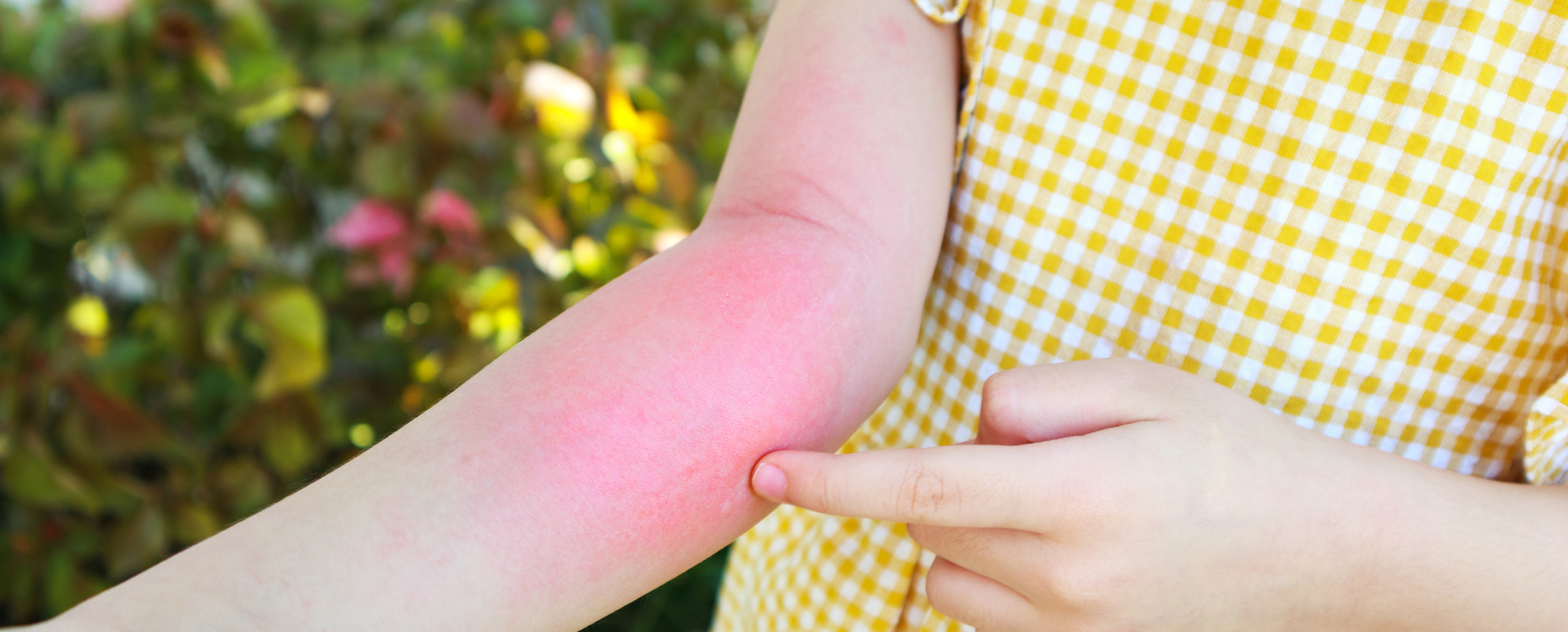

When the body is exposed to physiological doses of allergens and exhibits abnormal physiological dysfunction or tissue damage, it is referred to as a hypersensitivity reaction. This can be mediated by immune or non-immune mechanisms, with IgE-mediated immune responses specifically termed allergic reactions.
Allergic reactions occur rapidly and can affect a single system or the entire body. Common symptoms include itching, redness, swelling, and nasal discharge, while severe cases may lead to anaphylactic shock. Common allergic diseases include allergic rhinitis, asthma, atopic dermatitis/eczema, urticaria, allergic conjunctivitis, and allergic gastroenteritis.。
According to the World Allergy Organization (WAO), over 2.4 billion people worldwide are affected by allergic diseases, and the global healthcare burden of these conditions is rising sharply.

Global population affected by allergic disease

According to the World Allergy Organization (WAO), the global prevalence of allergic rhinitis
The prevalence of allergic rhinitis in China
Allergy Immunotherapy (AIT), originating in Europe, has a history of over 100 years. In 1911, Noon and Freeman successfully used pollen extract to treat hay fever in humans, marking the beginning of AIT. With the advent of evidence-based medicine, extensive research into the immunomodulatory mechanisms of AIT and substantial clinical data have increasingly supported the efficacy of two main immunotherapy methods: subcutaneous immunotherapy (SCIT) and sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT). Compared to conventional symptomatic treatments, AIT can significantly and long-term alleviate symptoms and reduce medication use in patients with moderate to severe allergic diseases, while also improving their quality of life.
Global guidelines, including those from the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Allergic Rhinitis and Its Impact on Asthma (ARIA), recommend incorporating AIT into the standard treatment protocols for airway allergic diseases. The WHO's Global Allergy Diseases Treatment Guidelines explicitly state that AIT is the most direct method of etiological treatment for allergic diseases. Both the Chinese guidelines for allergic rhinitis (AR) and the new guidelines for allergen immunotherapy (AIT) recommend early initiation of AIT for AR patients.

Crude extract mixtures derived from allergens
Administered via sublingual (drops, sprays, tablets) or subcutaneous injection
Low content of effective sensitizing proteins, high impurity levels, leading to poor treatment efficacy and safety
Current AIT products approved in China and Japan are first-generation products
Worg's wholly-owned subsidiary, Diater, currently offers sublingual and subcutaneous products covering over 40 allergens, with sales in more than 30 countries worldwide
Allergen polymers derived from natural extracts with special chemical modifications
Administered via sublingual, subcutaneous, or intradermal routes
Major AIT manufacturers in Europe have corresponding technological capabilities
Worg's wholly-owned subsidiary, Diater, currently offers polymerized products for over 20 allergens, with sales in more than 30 countries worldwide
Naturally purified molecular allergens with high molecular purity
Administered via subcutaneous injection
High content of effective sensitizing proteins, reduced side effects, and significantly improved treatment efficacy
Worg's globally exclusive technology platform
Utilizes recombinant fusion proteins/peptides, retaining only the sensitizing protein IgG induction sites
Significantly improved treatment efficacy with minimal side effects
Worg's clinical development progress is leading globally